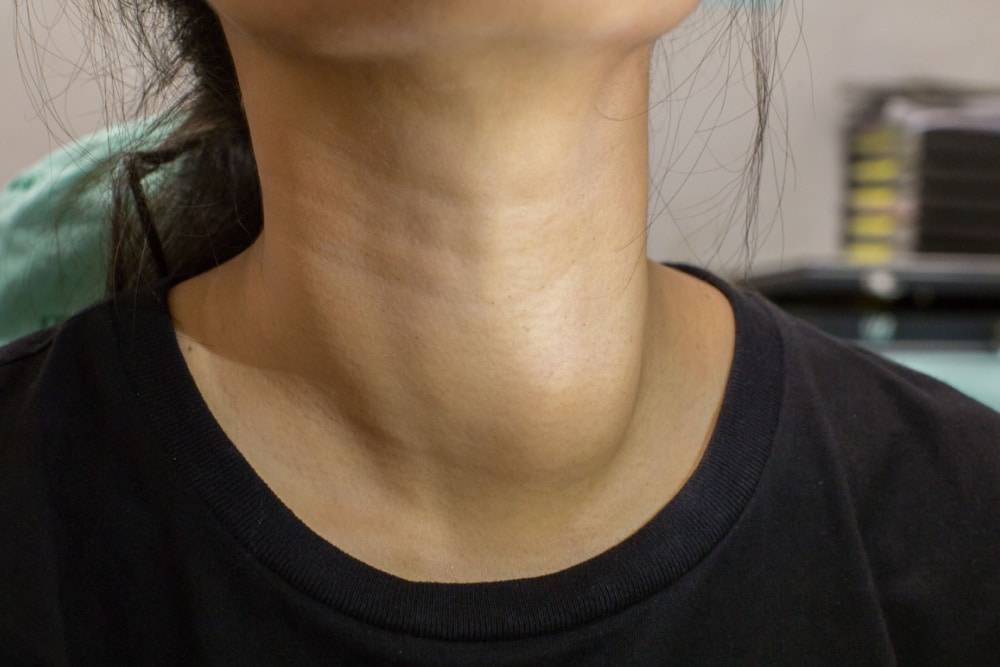
Thyroid nodules, lumps that form within the thyroid gland at the base of the neck, have become a focus for healthcare professionals and the public due to their prevalence and potential health implications.
While mentioning nodules may sound alarming, it’s essential to understand that most thyroid nodules are benign (non-cancerous) and often don’t lead to serious health issues. However, a small percentage can be malignant (cancerous), making awareness and appropriate management crucial. We also get insights from Dr Thomas Ho from Thomas Ho Surgery,
What Are Thyroid Nodules?
Thyroid nodules are growths that can appear in the thyroid gland, which plays a vital role in regulating the body’s metabolism through the secretion of hormones. These nodules can vary greatly in size and can either be felt as a lump in the throat or be asymptomatic, often discovered incidentally during a routine medical examination or imaging for unrelated reasons. Dr Ho added, “Not everybody has them, and it’s important to get them sorted out by a doctor or specialist.”
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of most thyroid nodules remains unknown, but several factors may increase the risk of developing them, including:
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is crucial for thyroid hormone production. A lack of it can lead to nodule formation.
- Gender and Age: Women and older adults are at higher risk.
- Dr Ho added, “thyroid nodules are very common in our population, especially women. It’s been estimated that up to 50% of women have thyroid nodules, whether they are aware of them or not. Prevalence in men is up to about 20-30%.”
- Genetic Factors: A family history of thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer increases the risk.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to radiation, especially during childhood, can increase the risk of thyroid nodules.
Dr Ho added that other dangers include “lymph nodes that could indicate a form of cancer, or it could be large enough to be causing any impending danger to the airway or the oesophagus.”
Symptoms to Watch For
Many thyroid nodules don’t cause symptoms and are non-palpable. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- A noticeable lump or swelling at the base of the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, depending on whether the nodule is producing thyroid hormones
Diagnosis and Evaluation
When a thyroid nodule is suspected, healthcare providers may use a combination of methods to evaluate it, including:
- Physical Examination: Palpation of the neck to feel for nodules.
- Ultrasound: Imaging to determine the size, composition, and appearance of the nodule.
- Blood Tests: To assess thyroid function.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy: To sample cells from the nodule, helping to determine if it’s benign or malignant.
Treatment Options
The treatment for thyroid nodules depends on their nature (benign vs. malignant), size, and whether they cause symptoms:
- Observation: Small, asymptomatic nodules may simply be monitored over time.
- Thyroid Hormone Suppression Therapy: In some cases, synthetic thyroid hormone is prescribed to attempt to shrink the nodule.
- Surgery: Nodules that are cancerous, suspicious for cancer, or cause significant symptoms may require surgical removal.
- Radioactive Iodine: Used to treat nodules associated with hyperthyroidism.
The Importance of Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential to detect any changes in size or characteristics. This proactive approach helps identify and address any potential problems promptly, minimizing the risk of complications.
Conclusion
Thyroid nodules are a common condition that can affect anyone but are most frequently seen in women and older adults. While the thought of a nodule can be concerning, understanding that the vast majority are benign and manageable can provide reassurance. It’s crucial to follow healthcare providers’ recommendations for monitoring and treatment to ensure the best possible outcome. Early detection and appropriate management are key to effectively handling thyroid nodules and maintaining optimal health.