UMMC’s non-invasive stroke recovery programme can help patients recover by modifying brain activity via electrical stimulation over 10 sessions in 2 weeks. They currently have the capacity to treat more patients and are urging stroke patients to get treatment.
Professor Dr. Mazlina Mazlan, a consultant rehabilitation physician in UMMC, shares that patients who were initially unable to form full sentences could do so after only ten sessions. The treatment can be completed as soon as two weeks, costing approximately RM2,000. It is free for pensioners and civil servants.
Understanding Stroke
A stroke happens when a blocked (ischemic stroke) or ruptured blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke) causes reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain. This can lead to loss of function in the affected area. A stroke can manifest in many ways, the common symptoms being:
- Weakness/ Inability to move one side of the body
- Headache
- Blurring of vision
- Dizziness, loss of coordination
- Confusion, unable to speak or understand speech
- Loss of consciousness
Stroke is Malaysia’s third leading cause of death and was one of the top 5 causes of hospital admissions from 2012 to 2019. It is expected to be the second leading cause of mortality in 2040. The general incidence of stroke has also increased, with about 40, 000 people being diagnosed annually.
An average of 92 stroke admissions occur daily across Malaysia, with approximately 32 expected deaths. 40% of these patients are less than 60 years old.
Risk Factors For Stroke
There are multiple risk factors that can increase one’s chances of getting a stroke. The main risk factors for stroke include:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High blood cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Ùnhealthy weight
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Stress
- Low fibre high-fat diet
- Heavy alcohol consumption
What To Do In Case of A Stroke
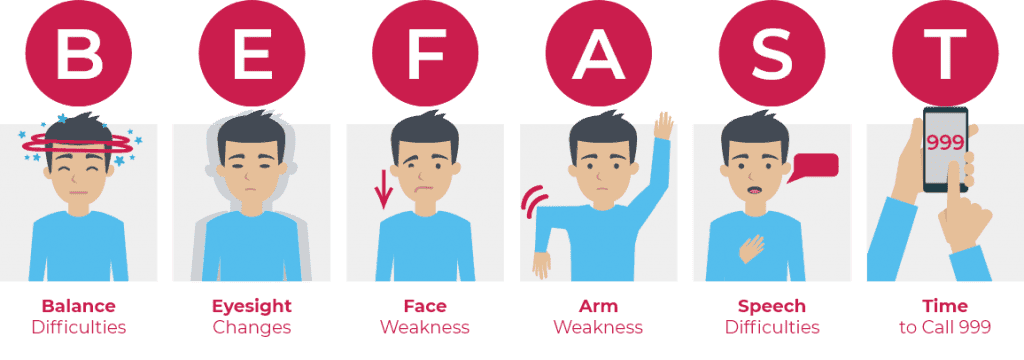
The Malaysian Stroke Council and the National Stroke Association of Malaysia (NASAM) recommend applying the B.E.F.A.S.T method. Effective intervention within the first 60 minutes of a stroke (the golden hour) can significantly reduce the severity of the stroke, permanent neurological damage and disability.
Failure or delay in receiving treatment can result in irreversible damage to the brain and is usually fatal in 80% of cases.
What To Expect After A Stroke
Some patients recover with almost no neurological deficits. They carry on with their lives and maintain treatment as prescribed by their physicians. Most patients, however, end up with some form of physical disability due to reduced or loss of function in certain areas of the body. Issues may range from moving their limbs to difficulty chewing/ swallowing. Many patients experience a combination of these issues. It usually depends on the area of the brain that was affected by the stroke.
This is why rehabilitation is of utmost importance for stroke patients. The residual effects of a stroke can be mitigated with timely and effective rehabilitation.
UMMC’s Stroke Recovery Programme
The UMMC’s stroke recovery programme involves the use of TDCS and TMS. Transcranial direct current stimulation (TDCS) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), are non-invasive brain stimulation techniques that help to modify brain activity and induce neuroplasticity, enabling the brain to adapt and recover. The treatment is non-invasive and takes about 20 to 40 minutes to complete. Both treatment options stimulate the brain to improve recovery after a stroke.
Dr. Mazlina said, “We can either use a weak electrical current to directly stimulate the brain cells (TDCS) or employ a magnetic field to induce electrical activity in the neurons’’. After the treatment session, patients are to undergo physical therapy and/ or speech therapy, depending on the residual neurological effects of their stroke.
Dr. Mazlina mentioned that the best time to initiate treatment would be within the first three months of the stroke. Patients who suffered from a stroke of moderate severity stand to benefit the most from the recovery programme. Patients with mild stroke often recover on their own in time while severe stroke cases are unsuitable due to the widespread damage to the brain.
Dr. Mazlina assures that the procedure is safe and is not to be confused with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), which is usually the misconception among patients.
Call For Action
Stroke causes many complications to both patients and caregivers. Therefore, an effective and timely treatment regimen serves to benefit patients in terms of recovery and quality of life. Patients should seek more information from their physicians before shying away from treatment modalities that may improve their lives.

