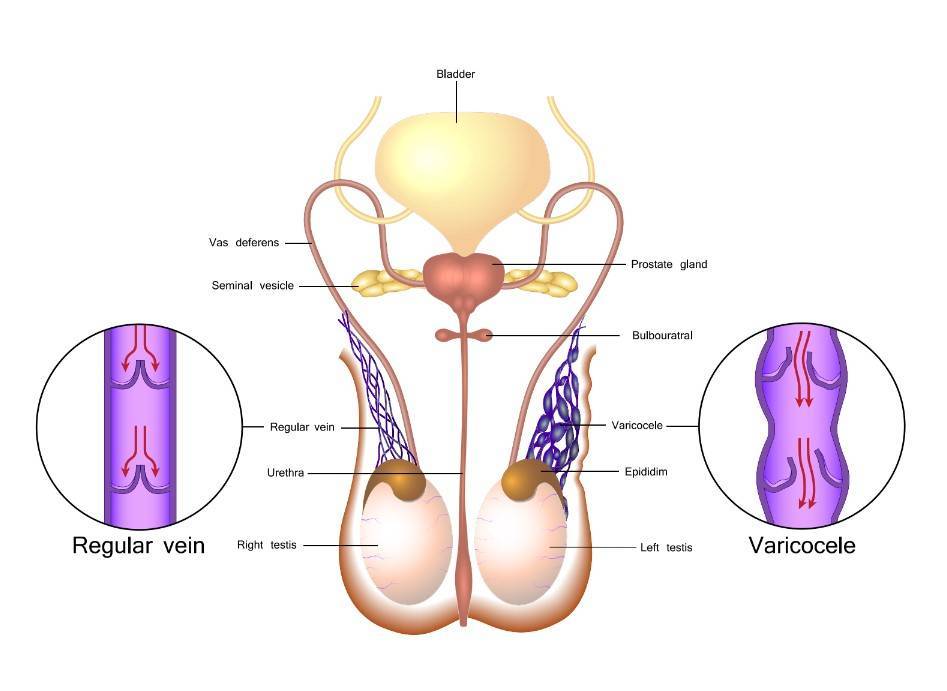
Varicocele is a condition in which the veins in the scrotum become swollen and enlarged. It is a common cause of infertility in men, affecting approximately 15% of all men.
In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of varicocele.
Causes
Malfunctioning valves in the veins carrying blood away from the testicles usually cause varicoceles. This malfunction causes blood to pool in the veins, leading to their enlargement. The exact cause of this valve malfunction is unknown, but there are several factors that can increase the risk of developing varicocele. These factors include:
- Age: Varicoceles are most common in men between the ages of 15 and 25.
- Genetics: Men with a family history of varicocele are more likely to develop the condition.
- Physical activity: Activities that increase abdominal pressure, such as weightlifting, can increase the risk of developing varicocele.
- Occupation: Certain occupations that require prolonged sitting or standing can increase the risk of varicocele.
Symptoms
Many men with varicocele experience no symptoms, but some may notice a dull ache or discomfort in the scrotum. In severe cases, varicocele can cause testicular atrophy (shrinkage) or infertility. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider.
Prevalence in Asia
In Asia, prevalence varies across different countries and populations, with studies reporting rates ranging from 7.4% to 15.7% among adult men. This variation can be attributed to differences in study methodologies, sample sizes, and population characteristics. Despite these disparities, varicoceles remain a significant health concern in the region,
Diagnosis
Firstly, a physical exam can usually diagnose varicocele. Your healthcare provider may also order an ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis and to rule out any other potential causes of your symptoms.
Treatment
If discomfort or infertility results from the condition, doctors may recommend treatment. The most common treatment options include:
- Varicocelectomy: This is a surgical procedure in which the swollen veins are tied off and cut to prevent blood flow. It is usually performed on an outpatient basis and has a high success rate.
- Embolization: This is a minimally invasive procedure in which a small tube is inserted into the groin and used to block the affected veins. It is usually performed under local anesthesia and has a shorter recovery time than surgery.
In some cases, varicocele may not require treatment, especially if it is not causing any symptoms or fertility issues. However, it is important to have regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor the condition
Conclusion
Finally, varicocele is a common condition that affects many men. While it may not always require treatment, it is important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms. Therefore, with the right diagnosis and treatment, most men with varicocele can successfully manage the condition and improve their quality of life.

