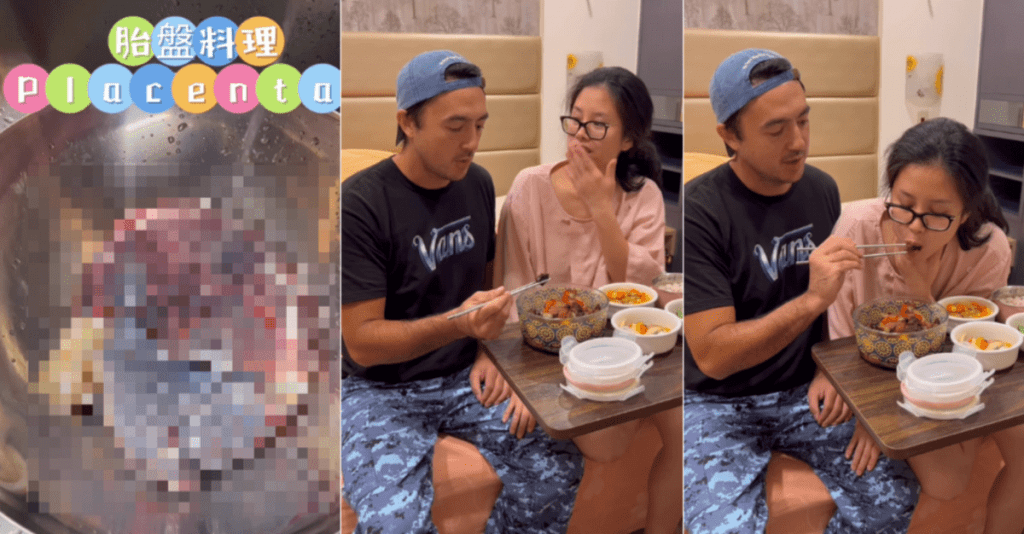
Placentophagy, or placenta eating, recently made news when Taiwanese actor Benjamin Wong took to Instagram to share a video of him preparing and stir-frying his wife’s placenta post-partum.
In the video, Wong described it as ‘tastes a little like pig’s liver’, with the wife saying it was ‘fishy’. Read more to know if there are medical explanations behind eating a placenta

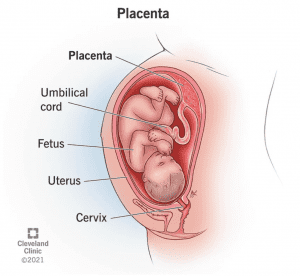
What is a placenta?
The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. It plays a crucial role in providing nutrients, and oxygen, and removing waste products from the developing fetus. The placenta forms from both maternal and foetal tissues and acts as a barrier between the mother’s blood supply and the baby’s blood supply. In simple terms, it’s a congregation of connective tissues with the endothelium of foetal blood vessels.
Why do people eat placenta?
For the older generation, placenta eating is nothing new. It has been observed in various cultures throughout history:
- Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM): Placentophagy has been a part of TCM for centuries. In TCM, the placenta is believed to have medicinal properties that can help replenish a woman’s energy and blood loss during childbirth, promote healing, and support postpartum recovery.
- Central India: the Kol Tribe eat the placenta to aid reproductive function since ancient times. However, this is not scientifically proven to be true.
- Some Native American cultures: Certain Native American tribes have traditions that involve honouring the placenta. In some tribes, the placenta is buried, while in others, it may be consumed as a way to connect the baby with its ancestral roots and provide spiritual protection.
- Some African cultures: Placentophagy has been reported in certain African cultures as part of postpartum rituals and practices. It may be consumed or used in various ways, often associated with beliefs in enhancing fertility, promoting bonding, or ensuring the health and well-being of the newborn.
In addition, many believe in its nutritional benefits, including iron, vitamins, and minerals. In times of poverty, it does provide important nutrients for the maternal body after childbirth. However, is this still necessary in modern times with the advancement in medicine?
Are there any health benefits?
With this question in mind, we consulted Internal Medicine Specialist Dr Henry Galuba of Mediclinic Middle East, here is what he has to say:
“The eating of the placenta scientifically has not been proven to have medical benefits. In fact, this is considered to be medical waste or biohazard material thus proper health precautions are taken with regard to its storage & disposal. Its medical benefits (for example, in TCM) is mainly based on cultural beliefs, instead of scientific research. Medical studies have proven that it can contain harmful bacteria if consumed, therefore extreme caution & restraint must be exercised in watching such social media posts. There are lots of sources of nutrition from a variety of food and supplements, so it’s better to go for what is scientifically proven rather than being convinced to try the unconventional.”
Further, it’s important to remind the public that the placenta contains human blood, along with potential blood born diseases. If not properly processed, consuming this can result in life-long infections.
Conclusion
Despite that, some might be curious about what it tastes like, but it is in general not recommended by the modern medical community for people to consume placenta in any way. Meanwhile, it does not provide any more superior or extra nutritional benefits compared to your daily food or supplements provided by your treating team.


