Sinusitis is a very common condition affecting the nasal passage. It is estimated that 12.5% of people around the world are affected by this condition. But a study conducted in 2009 in the USA showed that sinusitis is lower in the Asian population compared to African Americans and whites.
What is sinusitis?
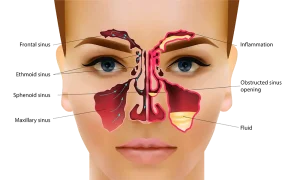
Sinuses are 4 pairs of hollow, air-filled cavities in the bones of the face and skull that are connected through narrow channels. These cavities have a soft tissue lining which produces mucus that usually drains out through the nasal passages, keeping them moist, free of dirt and germs.
Sometimes, the mucosal lining of the sinuses get inflamed and produce larger amounts of mucus, blocking the sinuses with fluid. This condition is called sinusitis.
Causes of sinusitis
Sinusitis is usually caused by an interplay of various factors. It is most commonly triggered by viral infection e.g. that which causes the common cold, and occasionally due to ensuing secondary bacterial infection.
The aforementioned contributory factors/risk factors include:
- Asthma
- Seasonal and nasal allergies e.g. to pollen, mould spores, dust, animal hair
- Abnormal nasal structure
- Nasal polyps (growths on lining of sinuses that can cause inflammation/obstruction)
- A deviated septum. The septum is the line of cartilage that divides your nose. A deviated septum means that it is closer to the nasal passage on one side of your nose, predisposing to blockage.
- A weak immune system from illness or medications.
- Smoking
- Respiratory infections
What are the symptoms of sinusitis?
The common symptoms of sinusitis are:
- Facial pressure, especially around the nose and eyes
- Headache
- Pain in teeth or ears
- Bad breath
- Stuffy nose
- Green or yellow nasal discharge
- Postnasal drip (mucus dripping down the throat)
- Fever, cough and fatigue
Depending on cause and duration of symptoms, sinusitis may be classified as:
Acute sinusitis
Acute sinusitis is an infection caused either by viruses or bacteria. A viral infection lasts for 1-2 weeks, whereas a bacterial infection lasts for up to four weeks.
Chronic sinusitis
Chronic sinusitis is typically caused by a bacterial infection, structural problems with the nose or immune dysfunction. It lasts for more than three months.
You should consult a doctor if:
- Symptoms of sinusitis do not subside within ten days.
- Symptoms do not improve even with medications
- You experience a fever lasting more than 3 days
- You have blurred/double vision; this may be an indication that infection has spread from sinuses to eyes
- Severe headache/ neck stiffness/ mental confusion; this may be an indication that infection has spread from sinuses to surrounding facial bones/brain
- Recurrent sinus infections (e.g. >4 times per year)
- Persistent sinusitis (e.g. >1 month)
- Loss of smell
- Blood stained nasal discharge
How is sinusitis diagnosed?
The doctor can make a diagnosis with the following:
- An account of your symptoms
- Feeling for tenderness in your nose and face
- Using an endoscope (A thin, flexible tube with a fibre-optic light inserted) to look inside nasal passages
- Imaging tests e.g. A CT or an MRI scan will reveal any structural problems like deviated septum, polyps, tumours which may not be visible through an endoscope.
- Collecting swab samples of your sinus discharge for cultures to determine the cause, such as bacteria or fungi for cases refractory to treatment.
- An allergy skin test to detect what allergen is responsible for your nasal flare-ups if allergies are suspected to be the main trigger for sinusitis
How is sinusitis treated?
Nasal solutions/sprays
- Irrigation with saline nasal sprays or solutions several times daily may help to clear the nasal passages.
- Corticosteroid sprays like fluticasone, budesonide and mometasone may also be prescribed for prevention and treatment of inflammation.
Allergy medication
- If the sinusitis is caused by an allergy, the doctor will prescribe medications e.g. antihistamines to reduce allergy symptoms.
Decongestants
- These may be in the form of sprays, drops or oral formulations. They help to relieve congestion and nasal obstruction but are only for short-term use e.g. for acute sinusitis, as overuse may result in rebound congestion.
Antibiotics/Anti-fungals
- If sinusitis is caused by bacteria/fungal infection, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics or anti-fungals respectively.
- In acute sinusitis, antibiotics are usually warranted if symptoms are severe, do not improve after 5 – 7 days or are recurrent.
- In some forms of chronic sinusitis, low-dose macrolide antibiotics is believed to have beneficial anti-inflammatory effect and may be prescribed for up to 3 months.
- Where possible, the choice of antibiotics should be guided by culture results of discharge samples obtained from the sinuses.
Medication to treat nasal polyps and chronic sinusitis
- If you have nasal polyps and chronic sinusitis, your doctor may give you an injection of dupilumab or omalizumab to treat your condition. These medications may reduce the size of the nasal polyps and lessen congestion.
Surgery
- If none of the above methods are effective, surgery may be required. Sinus surgery involves removing sources of blockage e.g. polyps, also enlarging narrow sinus openings to promote proper drainage. Infected sinus tissues and bones are also extracted.
What are some lifestyle changes to prevent or manage sinusitis?
- Go for recommended vaccinations (e.g. influenza vaccination, pneumococcal vaccintaions).
- Stay away from people with colds or respiratory infections.
- Practise good hand hygiene i.e. washing hands before meals.
- Take ample rest when down with a cold, to help your body to fight the infection and recover fast. While lying down, use a pillow to keep the head raised.
- Maintaining air conditioning units to prevent mould and dust from collecting
- Avoiding allergens where possible.
- Using a warm compress near your nose or face provides relief from symptoms.
- Steam inhalation is very effective in moistening the nasal passages and relieving the symptoms. You can add a few drops of essential oils like eucalyptus oil or menthol to the steam pot.
- Avoid smoking/inhaling secondhand smoke.
Conclusion
In most cases, sinusitis will subside on its own with proper rest and over-the-counter medications. In cases of severe, recurrent or persistent symptoms, it is best to consult a doctor for appropriate management.
