In a world increasingly focused on well-being, weight loss isn’t just about appearances anymore. It is also about investing in your long-term health and quality of life.
Beyond boosting self-esteem, maintaining a healthy weight can dramatically lower the risks of serious conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Yet, as global rates of overweight and obesity continue to climb, more people are facing challenges in achieving this goal.
Overweight and Obesity – A Growing Challenge
Overweight and obesity refer to having excess fat that increases the risk of serious health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, certain cancers, osteoarthritis and other complications. These conditions are growing global health challenges and require urgent attention.
Both overweight and obesity are emerging as public health challenges in most countries. In 2023, the prevalence of obesity in Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines were more than 20% while Singapore was about 11.6%.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a calculated measure of body weight in relation to height.
The BMI ranges can be categorised into underweight, normal, overweight or obese. Obesity is then further divided into three classes.
| BMI Category | BMI Range (kg/m²) |
| Underweight | Less than 18.5 |
| Normal | 18.5 to 24.9 |
| Overweight | 25 to 29.9 |
| Class 1 Obesity | 30 to 34.9 |
| Class 2 Obesity | 35 to 39.9 |
| Class 3 (Severe) Obesity | More than 40 |
Causes of Weight Gain
Unhealthy eating habit is a leading factor to excessive weight gain.
The causes of excess weight are complex and multifactorial. They can include:
- Unhealthy eating habits
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Genetic predisposition
- Environmental factors such as rapid expansion of fast-food outlets
- Poor sleep quality causing dysregulation of hormones controlling hunger urges
- Stressful lifestyle leading to ‘emotional eating’
- Medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hypothyroidism can cause people to gain weight
- Taking medications such as antidepressants, birth control, oral steroids and insulins
Watch also: Can Oral Contraceptives Cause Hypothyroidism? | Dr Henry Galuba Jr.
Steps to address overweight and obesity
Sometimes, individuals can face challenges in their weight loss journey like Lucian Teo who shared his struggles on our Community Page.
Sorry i think its v embarassing to ask this.
I am male, 35yo, n I fluctuate between 98-115kg depending on the time of the year. I am 175cm tall. yes I know I am fat. I have been trying over the last 5 years to lose weight, but I don’t know why i cannot…When i go below 98kg, I am very very hungry and grumpy to everyone. so I eat more and i gain back the weight easily.
I have tried OMAD, keto, everything. but nothing works. i know its hard to give more details in a post, just want to vent and see if anyone struggles like me. and for the drs, if you can tell me are there any weight loss magic. I heard about duromine and new prescription medicine like ozempic, but I’m scared of side effects. what about the balloon in the stomach, or bariatric surgery? anything to help will be great.
hope to hear from everyone, dr or not. tks.
Shedding extra weight may not be as easy as it seems! For overweight and obese individuals, it may require multifaceted and tailored approaches. Common strategies include lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgery or procedures.
1. Adopting Healthier Lifestyle Habits
- Change your diet
Dietary changes are the cornerstone of weight management. Start by controlling portion sizes and cutting back on foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats. You can consider exploring diets like the Mediterranean or high-protein Paleo diet to see if they are helpful in your weight loss journey. Meal replacements or intermittent fasting may also support weight loss goals.

“A crucial factor for sustainable weight loss is long-term calorie reduction in a manageable way, such as reducing daily intake by 300 calories.” shared Dr HC Lee, a general practitioner at Sigma Health, Singapore.
“This approach helps minimise mood disruptions. Successful patients often adopt lasting changes in eating behaviour and lifestyle to maintain their desired weight.”
Tip: Consult a doctor or dietician to seek guidance before adopting any weight loss diets, meal replacements or intermittent fasting, as they may have different effects to different individuals.
- Staying Active
Regular exercise boosts metabolism, helping to burn calories better and enhancing overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
Activities like brisk walking, running, cycling, and swimming are excellent for weight loss and improving health. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and strength training are also effective for shedding pounds and building muscle.

Tip: Start slow at first. Choose the exercise you enjoy doing, so you will be motivated to commit.
- Get sufficient sleep and manage stress well
Generally, it is advisable to get 7-8 hours of uninterrupted sleep every night. Insufficient sleep is associated to elevated levels of appetite-regulating hormone ghrelin. This causes individuals to eat more and put on weight.
Besides, stress leads to weight gain by triggering the release of cortisol hormone or commonly called the ‘fight-or-flight’ hormone.
Cortisol slows down the metabolism but increases the body’s insulin levels. Increased insulin drops the blood sugar levels, making you crave for more sugary foods.
Hence, for highly stressed individuals, it can be helpful to take steps to manage stress – whether it is via meditation, yoga, or even hanging out with friends.
Tip: Practice good sleep hygiene, and remember to take a break when you feel stressed!
Other than long-term calorie reduction in manageable ways, there are medical options available as well to support one’s weight loss journey.
2. Consider Weight-Loss Medications
For those finding lifestyle changes challenging, weight-loss medication can offer additional support. These medications aid weight loss by reducing fat absorption or suppressing appetite. However, they should be used strictly under a doctor’s guidance.
- Orlistat
It blocks the absorption of fat in the intestines.
- GLP-1 agonists (Liraglutide, Semaglutide)
Available in the form of oral medication and subcutaneous (under-the-skin) injections, the drugs mimics the glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) hormone. This hormone targets the brain areas controlling appetite to promote satiety. Hence, it can help to suppress appetite and reduce food intake.
- Naltrexone-Bupropion
A combined medication of a substance-use treatment (naltrexone) with an antidepressant (bupropion) to reduce cravings and control appetite.
- Phentermine
Commonly used for short-term treatment, it is an appetite suppressant that helps reduce hunger.
Despite being effective for weight loss, these medications may come with side effects such as gastrointestinal issues, headache, dizziness, and elevated blood pressure.
“All prescription medications come with benefits and risks, so a consultation with a medical doctor is essential to determine individual suitability.” cautions Dr. Lee.
Remember to only take prescribed medications for weight loss under doctor’s advice. (Shutterstock)
Tip: Always consult a doctor before taking any weight-loss medications. Do not buy any unlicensed slimming pills from websites or shops as they may contain dangerous substances.
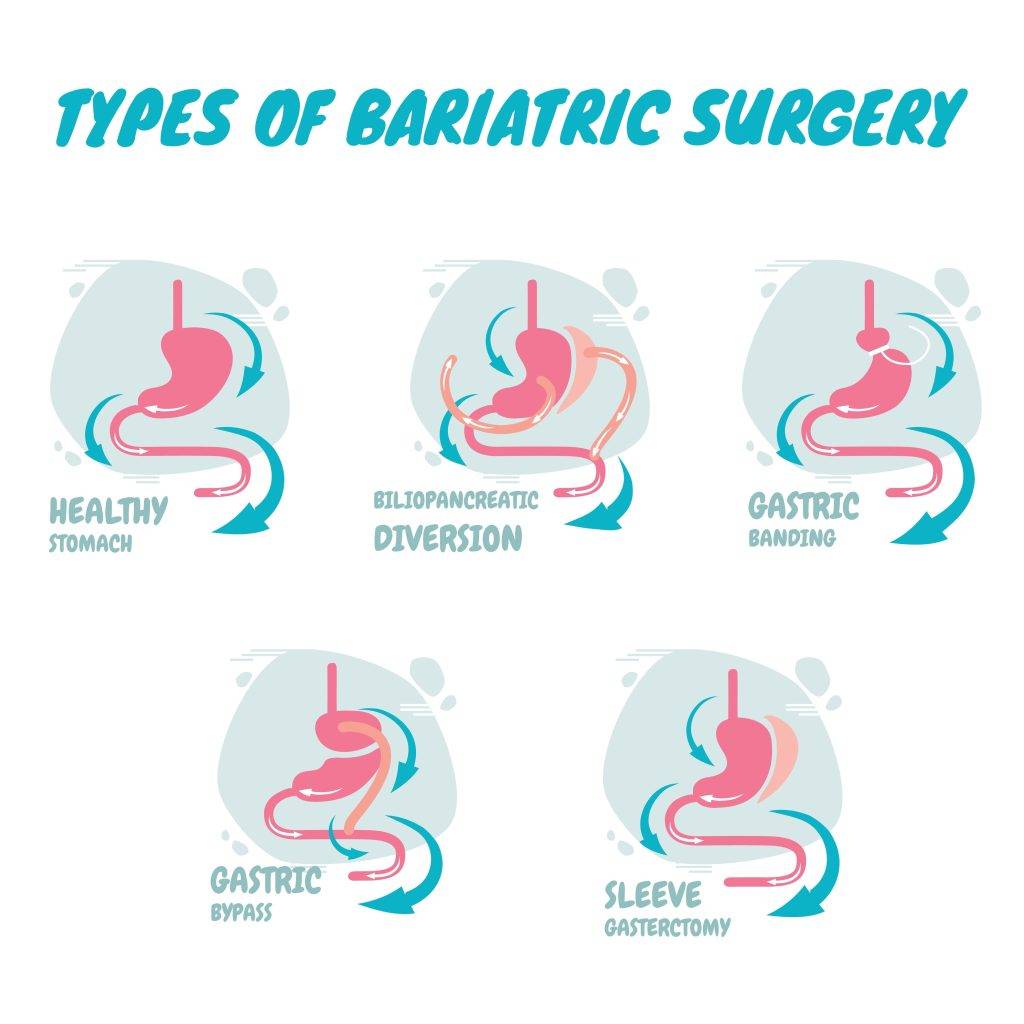
3. Surgery and Procedures for Weight Loss
When lifestyle adjustments and medications are not enough, bariatric surgery or endoscopic procedures may be recommended by the healthcare team for effective weight loss. This is especially true for those with severe obesity.