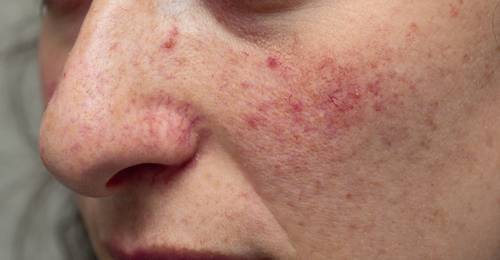
Rosacea, a chronic and often misunderstood skin condition, affects millions of people worldwide, with a significant number of cases emerging in Asia.
Characterised by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and acne-like bumps, rosacea can cause discomfort and self-consciousness in sufferers. This article aims to shed light on rosacea, its triggers, treatments, and how it impacts the Asian population.
More Than Just a Blush
Rosacea typically affects adults between the ages of 30 and 60, with fair-skinned individuals at higher risk. However, in recent years, an increasing number of cases have been reported among the Asian population. While the exact cause of rosacea remains unknown, experts believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors, along with immune system abnormalities, contribute to its development.
Triggers and Aggravators: Igniting the Flames
Various factors can trigger or worsen rosacea symptoms, and identifying these triggers is crucial for effective management. Common rosacea triggers include:
- Sun exposure
- Spicy foods
- Hot drinks
- Alcohol consumption
- Stress
- Extreme temperatures
- Skincare products with harsh ingredients
It’s essential for sufferers to monitor their reactions to these factors and modify their lifestyle accordingly to minimise flare-ups.
Symptom Spectrum: The Four Faces of Rosacea
Rosacea presents in four distinct subtypes, each with unique symptoms:
- Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR): Characterised by facial redness and visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular rosacea: Resembles acne, with red bumps and pus-filled pimples.
- Phymatous rosacea: Causes thickened, bumpy skin, often affecting the nose.
- Ocular rosacea: Affects the eyes, leading to redness, irritation, and swollen eyelids.
A proper diagnosis by a dermatologist is essential to identify the specific subtype and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Approaches: Taming the Redness
While there is no cure for rosacea, a range of treatments can help manage symptoms and improve skin appearance. Treatment options include:
- Topical medications: Creams or gels containing antibiotics, azelaic acid, or ivermectin can reduce redness and inflammation.
- Oral medications: Antibiotics, such as tetracycline or doxycycline, can help control moderate to severe symptoms.
- Laser therapy: Intense pulsed light (IPL) and other laser treatments can diminish visible blood vessels and redness.
- Skincare routine: Adopting a gentle skincare regimen, using fragrance-free and non-abrasive products, can help soothe sensitive skin.
A dermatologist can recommend the most suitable treatment options based on the individual’s specific subtype and severity.
Coping Strategies
Living with the condition can be challenging, but adopting certain strategies can help improve the quality of life for sufferers:
- Identifying and avoiding triggers
- Wearing sun protection daily
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
- Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups
Conclusion: Unveiling a Clearer Complexion
Once considered a predominantly Western condition, the condition has been increasingly diagnosed in Asia, highlighting the importance of awareness and education. Therefore, by understanding rosacea’s triggers, symptoms, and treatment options, those affected can take charge of their condition, minimise flare-ups, and unveil a clearer, healthier complexion.