Do you or your partner often snore loudly at night? Or feel very sleepy during the day despite getting enough sleep? If so, you may need to understand more about Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA).
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnoea?
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA) is a serious sleep disorder characterised by repeated pauses in breathing due to blockage of the upper airway. During sleep, the throat muscles relax, which can cause the airways to narrow or even close, disrupting airflow.
This condition can cause sufferers to stop breathing for a few seconds up to hundreds of times a night, potentially resulting in a lack of oxygen in the body.
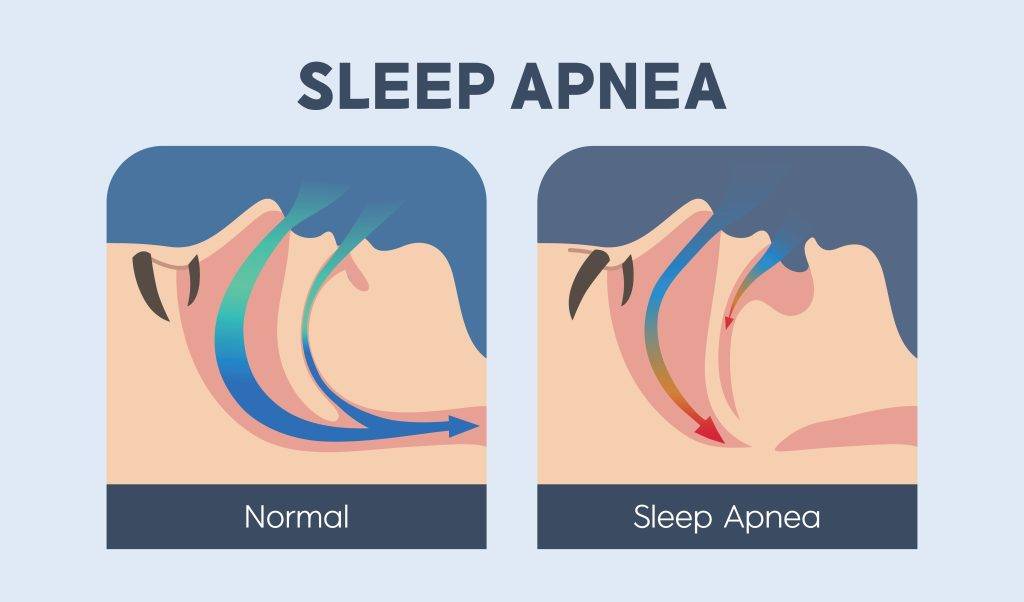
repeatedly during sleep,
Watch this: Dr Valerie Tay – Obstructive Sleep Apnoea OSA
Types of Sleep Apnoea
There are different types of sleep apnoea
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA) is the most common form of sleep apnoea, where the airway is blocked by soft tissue in the throat. In OSA, the throat muscles become too relaxed during sleep, causing the airway to narrow or close, interrupting airflow.
- Central Sleep Apnoea (CSA) is a sleep disorder where the brain fails to send the right signals to the muscles that control breathing, causing repeated periods where one stops breathing during sleep.
- Complex Sleep Apnoea is a combination of OSA and CSA. Some patients with OSA may develop CSA while using positive airway pressure therapy, such as CPAP.
Symptoms of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea You Need to Watch Out for
Do you (or your loved one) suspect you have OSA? Here are the common symptoms that are often experienced by patients with OSA:
- Loud snoring
This is the most common sign of OSA. If your partner frequently complains about the sound of your snoring, this could be an indication of a problem.
Severe snoring such as that from OSA can cause anger and resentment in a partner, which in turn, may further impact sexual function and intimacy.
- Pauses in breathing
If someone sees you stop breathing during sleep, this is a serious signal that needs attention. These occurrences are often noticed by others.
- Daytime fatigue
If you feel sleepy throughout the day despite getting enough sleep, OSA may be the culprit. This sleep disorder can cause you to wake up many times during the night, resulting in poor sleep quality.
- Difficulty concentrating
Lack of quality sleep can lead to difficulty focusing and memory impairment.
- Morning headaches
Many people with OSA report experiencing headaches upon waking. This could be due to the lack of oxygen the brain receives during sleep.
- Mood swings
Sudden mood swings can occur due to sleep disturbances. Sufferers may feel more irritable or experience unusual emotional changes.
Who is at Risk for OSA?
Sleep apnoea can affect anyone, even children. Some factors that increase the risk of developing obstructive sleep apnoea include:
Obesity
Obesity, especially excess weight in the neck area, is a major risk factor for OSA. Fat accumulation around the airway can narrow the airway, increasing the chances of obstruction during sleep.
Male gender and older age
Men above the age of 40 are more prone to OSA. Women are also at high risk, especially after menopause, when hormonal changes can affect the throat tissue and increase the chances of obstruction.
Family History
A family history of OSA can increase your risk of developing the same condition. If any family member has this sleep disorder, you may also be at high risk.
Anatomical Factors
An individual’s physical structure, such as small tonsil size or jaw, may contribute to OSA risk. For example, enlarged tonsils or a poorly developed jaw can obstruct the upper airway more easily, resulting in OSA.
Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions such as hypertension, diabetes and heart disease can also increase the risk of OSA. These conditions often go hand in hand.
Research shows that sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes affect each other in both directions. This bidirectional relationship means that having one condition increases the risk of developing the other condition, and having both conditions makes each other worse over time. Older studies found that around 7 out of 10 people who have type 2 diabetes also deal with obstructive sleep apnoea.
Long-term Health Effects of OSA
Undiagnosed and uncontrolled OSA can be dangerous in the long run, leading to significant health risks including:
- Cardiovascular disease
OSA may increase the risk of hypertension, arrhythmia and heart attack.
Research shows that individuals with OSA have a higher chance of developing cardiovascular disorders due to fluctuations in oxygen in the blood that occur during apnoea episodes. This can lead to increased blood pressure and workload on the heart.
- Type 2 diabetes
Lack of quality sleep due to OSA can disrupt glucose metabolism and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. Research shows that prolonged sleep disturbances can affect insulin sensitivity, thereby increasing the likelihood of developing diabetes in individuals with OSA.
- Mental health problems
Poor sleep quality due to OSA contributes to mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. People with OSA often have difficulty in maintaining good quality sleep, which can worsen their mental state.
- Stroke
Research shows that OSA significantly increases the risk of stroke, particularly when left untreated. Individuals with severe OSA, defined by an Apnoea Hypopnea Index (AHI) of 30 or more, are at a higher risk of experiencing a stroke compared to those without OSA.
Some studies suggest that the risk of stroke in individuals with severe OSA can be up to twice that of individuals without the condition.
- Infections
Untreated sleep apnoea leads the body to a state of chronic low-grade inflammation and immune system activation. This chronic inflammation can impair immune responses and respiratory defence mechanisms, making sleep apnoea patients more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections that cause lower respiratory tract illnesses.
Additionally, untreated sleep apnoea is linked to changes in the airway microbiome and an increased risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease and chronic aspiration, further exposing the lungs to microbial pathogens.
- Decreased quality of life
Sleep disorders such as OSA can affect work productivity, social relationships and overall quality of life. Sufferers often feel tired and fatigued during the day, which negatively impacts their daily activities and social interactions.
Tips To Prevent OSA
Preventing OSA is much better than treating it. Here are some simple steps you can take everyday to manage your risk of developing OSA:
- Maintain an ideal body weight
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the airway. Research shows that weight loss can help reduce OSA symptoms, especially in obese individuals.
- Exercise regularly
Physical activity, especially cardio exercise such as running or cycling, is not only beneficial for physical health but can also improve sleep quality. Regular exercise helps burn calories and fat, and improves mental health. However, you should avoid exercising too close to bedtime to avoid disturbing your sleep pattern.
- Sleep on your side
Sleeping on your side can help prevent airway obstruction. Using an extra pillow to support this position is also recommended, as the tilted position reduces the chances of obstruction.
- Avoid alcohol and sleep aids
Alcohol consumption and sleeping pills can worsen the symptoms of OSA. Both can cause excessive relaxation of the throat muscles, which increases the risk of sleep apnoea. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid both of these, especially near bedtime.
If you have been prescribed sleeping pills by your doctor, discuss with them your symptoms to see if there are alternatives available for you.
- Create a Comfortable Sleeping Environment
@medicalchannelasia Today is World Sleep Day 😴 and adults need 7 or more hours a day! If you find it hard to sleep, you can try these 4 tips – and tip #4 is the most important one! 🤪 do YOU have trouble sleeping? Have you tried any of these? #worldsleepday #worldsleepday2022 #sleep #sleepday #sleepdeprived #learningisfun #health #healthy #medicaleducation #insomnia #insomniahacks #sleeptips #pharmacistsoftiktok ♬ Healing, sleeping, calming music box(999159) – Kei
Creating a comfortable sleeping environment is very important to improve sleep quality. Make sure the bedroom is dark, cool and quiet. Setting a favourable atmosphere for quality sleep can help you fall asleep faster and sleep better.
Untreated OSA can seriously impact health, increasing the risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, strokes and infections over the long-term. By recognising the symptoms, understanding the risks and taking action through lifestyle changes or treatment, you can improve your quality of life.
References:
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sleep-apnoea/symptoms-causes/syc-20377631
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/types-of-sleep-apnoea
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/the-dangers-of-uncontrolled-sleep-apnoea
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459252/
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/sleep-apnoea

