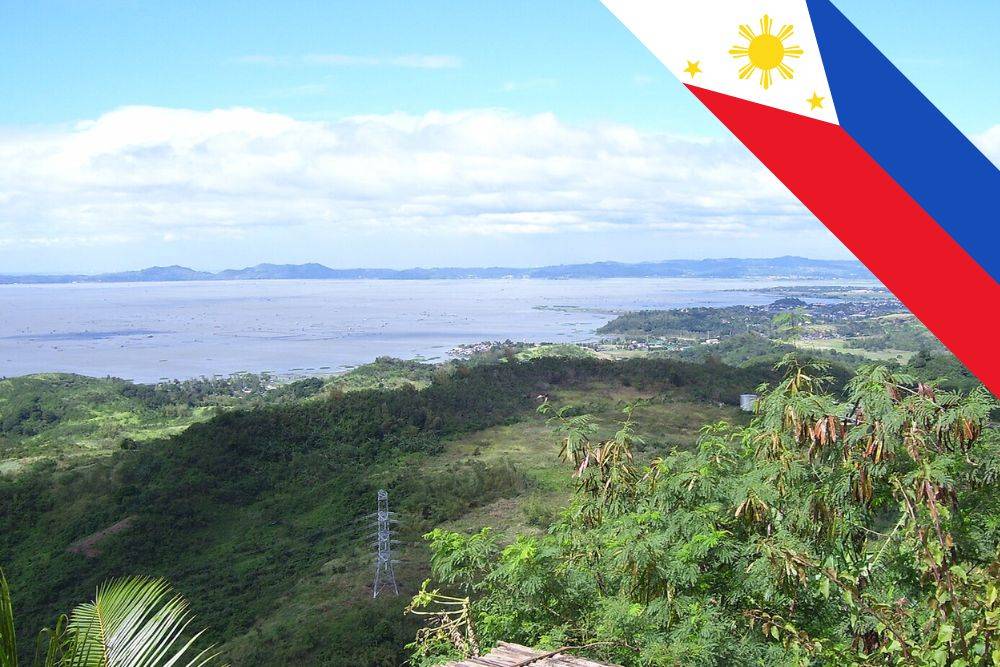
The Philippines’ largest lake, Laguna de Bay, is on the brink of an environmental and public health disaster.
Pollution, overfishing, and invasive species threaten Laguna de Bay, which has profound implications. They also affect the ecosystem and the human health of the communities surrounding it.
Pollution Crisis and Human Health
Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and untreated sewage are major pollutants contaminating Laguna Lake. Factories discharge heavy metals, chemicals, and other pollutants directly into the water. Moreover, agricultural activities contribute to the problem through pesticide and fertilizer runoff, which leads to nutrient overload and eutrophication. Additionally, many communities lack proper sewage systems, resulting in untreated human waste being dumped into the lake.
Consequently, the health implications of this pollution are severe. Contaminated water poses significant risks, including skin diseases, gastrointestinal illnesses, and respiratory problems. Heavy metals like lead and mercury can accumulate in fish, which, when consumed by humans, can cause neurological and developmental disorders, particularly in children. Furthermore, the toxic environment affects not only the wildlife but also the health and livelihood of the people who depend on the lake for fishing, drinking water, and recreation.
Overfishing and Its Impact on Food Security
Overfishing and the use of illegal fishing methods, such as fine mesh nets and electrofishing, have led to the depletion of fish stocks. This not only disrupts the lake’s ecological balance but also threatens the food security of local communities. Fish is a primary source of protein for many families, and the decline in fish populations means less food and nutrition available to them.
The economic impact of overfishing worsens health issues. Many families rely on fishing as their primary source of income. With dwindling catches, their livelihoods are threatened, leading to increased poverty. Poor economic conditions often correlate with poor health outcomes, as affected families may not afford adequate healthcare or nutritious food.
Invasive Species and Human Health Risks
Invasive species, such as the janitor fish, have proliferated in Laguna Lake. These species outcompete native fish, further destabilizing the lake’s ecosystem. The presence of invasive species disrupts the natural food web and leads to the decline of native fish populations. This not only affects biodiversity but also impacts the fishing industry, which relies on native species.
Invasive species can also be vectors for diseases. For instance, the proliferation of certain invasive fish can lead to an increase in waterborne pathogens, posing direct health risks to humans who come into contact with the water or consume contaminated fish.
Government and Community Response
In response to the crisis, various measures are being implemented by the government and local communities. The Laguna Lake Development Authority (LLDA) has introduced stricter regulations on industrial discharges and is promoting sustainable agricultural practices to reduce pollution. Environmental groups and community organisations are also actively involved in clean-up drives and awareness campaigns to educate the public about the importance of preserving the lake.
Improving waste management infrastructure in surrounding communities to reduce sewage pollution is crucial for protecting human health. Research institutions are studying the lake’s ecosystem to develop sustainable fishing practices and effective strategies for managing invasive species.
Conclusion
Laguna de Bay is at a critical juncture. The combined impact of pollution, overfishing, and invasive species is pushing the lake towards ecological collapse, with severe consequences for human health. Immediate and coordinated action is necessary to prevent further degradation and restore the lake’s health. This requires a holistic approach that includes stringent regulation, community engagement, and sustainable practices. The future of Laguna Lake depends on the collective effort of the government, communities, and individuals to protect and preserve this vital natural resource. Without significant intervention, the consequences could be devastating for both the environment and the health and well-being of local populations.
Have a pressing question for a doctor? Medical Channel Asia has launched a community forum page where you can get questions answered by a medical specialist. Visit the community forum here.