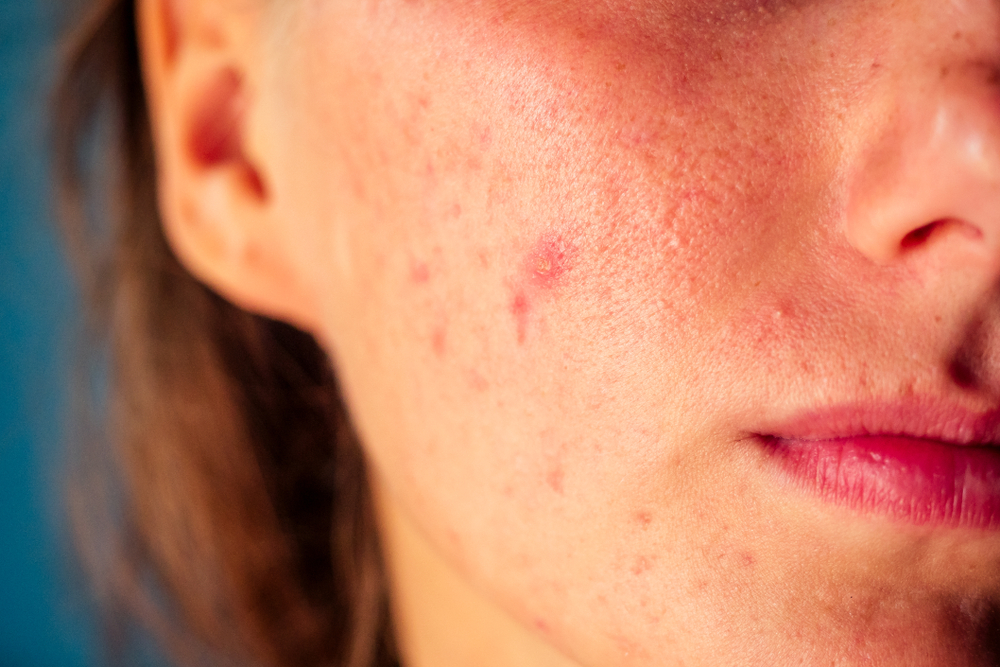
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people around the world. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads.
While acne is not a life-threatening condition, it can cause significant distress and have a negative impact on self-esteem. In this article, we will discuss the causes, treatments, and prevention strategies for acne.
What Causes Acne?
The condition is caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Excess oil production
- Clogged hair follicles
- Bacteria
- Inflammation
- Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy can also contribute to the development of acne.
Excess oil production: The sebaceous glands in the skin produce an oily substance called sebum, which helps to keep the skin lubricated and healthy. However, excess sebum production can cause the hair follicles to become clogged, leading to the formation of pimples.
Clogged hair follicles: Dead skin cells can accumulate in the hair follicles, leading to clogging. This can happen when there is an overproduction of skin cells, or when the skin does not shed properly.
Bacteria: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) is a type of bacteria that lives on the skin and feeds on the sebum produced by the sebaceous glands. When the hair follicles become clogged, the bacteria can multiply rapidly, leading to inflammation and the formation of pimples.
Inflammation: When the body detects bacteria in the hair follicles, it triggers an inflammatory response to fight the infection. This can cause redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area.
How is Acne Treated?
There are several treatments available for acne, ranging from over-the-counter products to prescription medications. The goal of treatment is to reduce oil production, unclog hair follicles, and kill the bacteria that cause inflammation.
Over-the-counter products: Many over-the-counter products are available to treat acne, including cleansers, creams, and gels. These products contain ingredients such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and alpha-hydroxy acids, which can help to unclog hair follicles and reduce inflammation.
Prescription medications: For more severe cases of acne, prescription medications may be necessary. These include topical retinoids, which can help to unclog hair follicles and reduce inflammation, and oral antibiotics, which can kill the bacteria that cause acne. In some cases, hormonal therapy may be recommended to regulate hormone levels and reduce oil production.
Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin is a prescription medication that is used to treat severe acne. It works by reducing the amount of oil produced by the sebaceous glands, and is highly effective in clearing up acne. However, it can have serious side effects, including birth defects, so it should only be used under the supervision of a doctor.
Prevention Strategies
While acne cannot always be prevented, there are several strategies that can help to reduce the risk of developing acne or prevent it from getting worse.
Wash your face regularly: Washing your face twice a day with a mild cleanser can help to remove excess oil and dead skin cells, and prevent the hair follicles from becoming clogged. Avoid using harsh scrubs or cleansers, as these can irritate the skin and make it worse.
Avoid touching your face: Touching your face can transfer bacteria from your hands to your skin, leading to inflammation and the formation of pimples. Try to avoid touching your face as much as possible.
Use non-comedogenic products: Non-comedogenic products are less likely to clog the hair follicles, and can help to reduce the risk of developing acne. Look for products that are labelled non-comedogenic or oil-free, and avoid using heavy makeup or moisturizers that can clog the pores.
Maintain a healthy diet: While there is no direct link between diet and acne, some studies suggest that certain foods may trigger or worsen the condition. Foods that are high in sugar or refined carbohydrates, such as cakes, cookies, and white bread, may increase insulin levels and lead to increased oil production. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to maintain healthy skin.
Manage stress: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that can contribute to the development of acne. Try to manage stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
While these strategies may work for some, they may not be effective for everyone. Acne is nuanced and requires specific care tailored to each person’s individual needs. There are many contributing factors, including genetics, hormonal imbalances, and lifestyle choices, making it a challenging condition to treat. Additionally, not all acne is the same, and different types of acne require different treatments.
It’s important to consult with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the underlying causes and provides the most effective care for your skin.