You may have heard about urinary tract infections (UTI) before, a condition that is more common in females than males due to a reason, which we are just about to share. In fact, it is said that at least 40% of all women will experience an episode of UTI in their lives, while only about 12% of men will.
So what is a Urinary Tract Infection?
An infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system is known as urinary tract infection. The urinary system includes four major components, namely the kidneys, ureters, bladder and a urethra.
 The purpose of the urinary tract is to form, store and expel urine from the body. The kidneys are found at the back of the pelvis, and work as “filters of the body”. They extract and remove waste material from the blood, and create urine. The ureters are then thin tubes that bring the urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder acts as a bag that stores the urine before we let it out. To do that, urine flows through a urethra, which is a tube that runs from the bladder to the outside of our bodies .
The purpose of the urinary tract is to form, store and expel urine from the body. The kidneys are found at the back of the pelvis, and work as “filters of the body”. They extract and remove waste material from the blood, and create urine. The ureters are then thin tubes that bring the urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder acts as a bag that stores the urine before we let it out. To do that, urine flows through a urethra, which is a tube that runs from the bladder to the outside of our bodies .
Hopefully, it is now easier for you to grasp the idea of a UTI after knowing how the different parts work.
In essence, a person develops UTI when microbes travel from the external environment, into the urinary tract. This infection then starts an inflammatory response by the immune system, leading to irritation and pain. Bacteria are usually the main culprits of UTI, although in some cases, viruses and fungi can also cause it.
There are two main types of UTIs. Upper UTI refers to the infection of the kidneys and are usually more severe, likely requiring closer monitoring and professional help. An infection involving the components below the kidneys, is referred to as lower UTI.
Risk factors that may lead to UTI
- Drinking less water and other fluids
- Holding urine for longer periods of time
- Inability of the bladder to empty regularly, such as with certain neurological diseases
- Blockage anywhere along the urinary tract, e.g. by kidney stones
- Sexual intercourse
- Women who use diaphragms, or spermicidal agents as birth control,
- Other diseases that either directly affect the immune system, or require medical interventions that lowers the immune system response to a bacteria infection e.g. cancer requiring chemotherapy, HIV/AIDS, diabetes mellitus
- Hormonal, and physical changes in the urinary tract during pregnancy, or at menopause, that makes women more prone to bacterial infections.
- Insertion of a urinary catheter
A woman is also more prone to UTIs compared to men, due to her anatomy where her urethra is comparatively shorter in length and positioned closer to the anus, which gives easier access to bacteria to reach the bladder.
Symptoms of UTI
- Fever and fatigue
- A burning sensation / pain during urination
- Urge to urinate more frequently, but only small amounts are passed at a time
- Urine may appear cloudy
- Urine may appear red / dark coloured due to the presence of blood
- Foul-smelling urine
- Abnormal discharge
- Pain of the pelvic region, and sometimes radiating to the back
- Discomfort / pain during sexual intercourse
How UTIs Are Being Treated
If an episode of UTI is found by chance, and the patient remains asymptomatic, there is no need for treatment. However, if a patient experiences the above symptoms, the usual choice of treatment for a bacterial UTI is antibiotics, and a fungal UTI, a course of antifungals. These medications have to be taken for a fixed duration, usually up to 2 weeks, but no less than what was prescribed.
If someone experiences recurrent UTIs despite other lifestyle modification efforts, they may be prescribed a longer course of antibiotics, usually at a lower dose to be taken regularly.
Effective Ways To Prevent UTIs
Following are some tips to avoid getting a UTI:
- Drink more water – this ensures that the urine in the bladder is more diluted and bacteria that may be residing or flushed out more regularly.
- Do not hold your bladder for prolonged periods of time.
- Wipe from front to back after using the toilet, to prevent transmitting bacteria from the anus to the urinary tract.
- Avoid feminine products that are irritating in nature with excessive scents.
- Always keep your genital area dry after using the toilet.
- After a workout, rinse or change out of perspiration-soaked underwear.
- Wear 100% cotton underwear and avoid tighter fits – this ensures a more breathable environment for your genital area as bacteria thrive in moist conditions.
- Review your birth control methods: avoid diaphragms, unlubricated or spermicidal condoms that have a greater tendency to encourage bacterial growth.
- Prior to sexual intercourse, it is recommended that both partners clean their genital areas to minimise the bacteria load. After sexual intercourse, urinate to remove bacteria that may have entered the urinary tract.
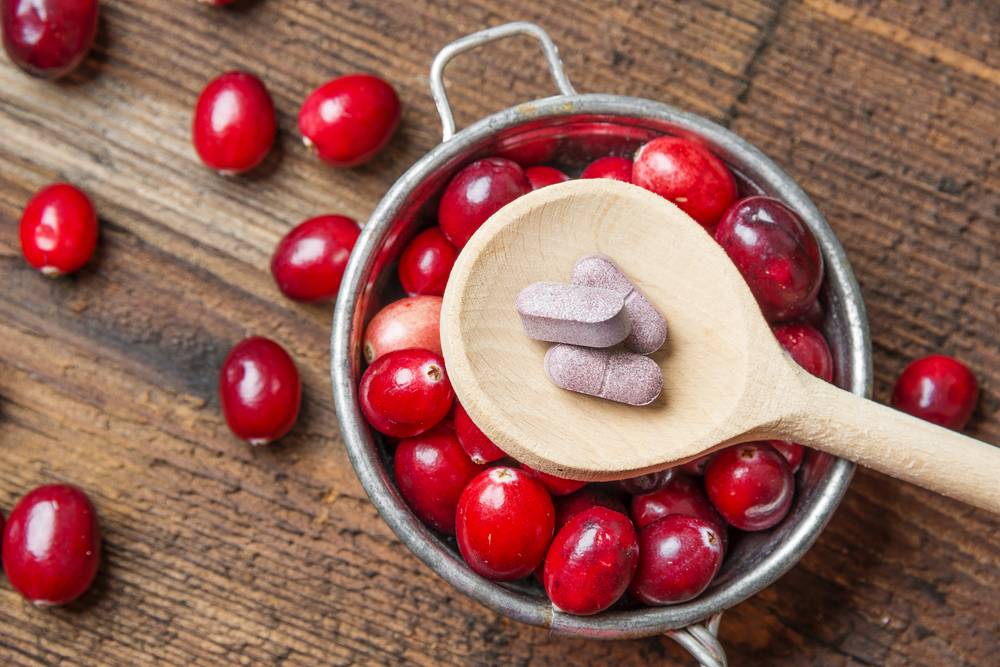
- Cranberries (in the form of the fruit, juice, and tablets) and probiotics may be useful as dietary supplements to minimise chances of getting a UTI. Cranberries prevent the bacteria from adhering to the walls of the urinary tract, reducing the chance of an infection. Probiotics generally help regulate a healthy, balanced bacterial flora to combat external infections.
Hopefully, the advice above will help you understand the importance of good personal hygiene and important habits to help minimise getting UTI. However, if you experience any of the symptoms, or realise that you have been contracting UTIs recurrently, do not solely rely on home-remedies, but seek the medical help of a doctor. If left untreated for a prolonged period, UTIs have the capacity to affect the function of your kidneys, and cause greater harm on your body.